Carbon offset and credit: key tools for reducing emissions
Carbon offset
A carbon offset refers to a reduction or removal of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions or an increase in carbon storage. This is achieved through different methods used to compensate for emissions.
Carbon credit
Carbon credit is a transferable instrument certified by governments or independent certification bodies. One carbon credit represents an emission reduction of one metric ton of CO2, or an equivalent amount of other greenhouse gases.
Carbon markets
Carbon credits are designed to provide a financial incentive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. These credits can be bought and sold in specific markets, known as compliance markets. Compliance markets are regulated by governments or other authorities.
Additionally, carbon credits can also be traded on the Voluntary Carbon Markets (VCM), where individuals and businesses can voluntarily participate in emissions reduction efforts.
Voluntary Carbon Market
The Voluntary Carbon Market is not regulated by governments or supranational institutions but by private organizations such as Verra or The Gold Standard which certify carbon offsets into carbon credits.
To ensure the quality and credibility of the VCM, these organizations apply rigorous methodologies and require the involvement of third-party auditors. The auditors are responsible for verifying the legitimacy and accuracy of the carbon offset projects.
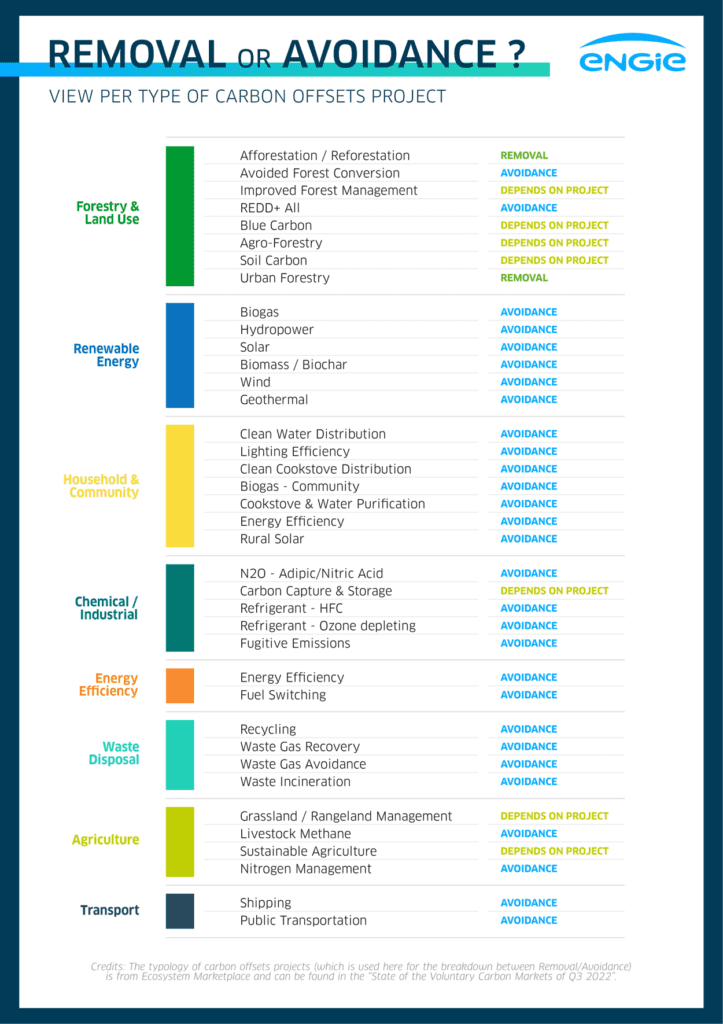
The differences between avoidance & removal offsets
Carbon offsets play a key role in achieving carbon neutrality or net-zero targets. There are two different types of offsets: avoidance and removal offsets.
Avoidance offset
An avoidance offset refers to a reduction in CO2 emissions compared to a baseline scenario, such as:
- Preserving standing forests that would otherwise have been cut down,
- Installing renewable power plants to reduce reliance on fossil fuels,
- Implementing energy-efficient solutions to reduce energy consumption.
As an example, ENGIE has a long-term partnership with ATEC for an avoidance offset project. The goal is to offset emissions through ATEC’s patented solutions, and our role is to support ATEC with the highest level of carbon accounting integrity.
Removal offset
Removal offsets address CO2 emissions that are already in the atmosphere. Removal projects provide solutions that capture and sequester greenhouse gases that are already present in the atmosphere. Here are some examples of removal offset projects:
- Planting trees in areas with no forests (afforestation) or restoring forests on land that was previously deforested (reforestation). These reforestation projects are also called Nature-Based solutions.
- Installing Direct Air Capture (DAC) technology to capture CO2.
- Fertilizing oceans by adding nutrients to stimulate the growth of algae and capture the CO2 from the water.
Environmental benefits and business opportunities through carbon offset strategies
Carbon offsets not only help reduce greenhouse gas emissions but can also have positive impacts on the environment, biodiversity, public health, and local communities.
At ENGIE, we can assist you in building a carbon offsetting strategy by providing high-quality carbon offsets, along with best-in class certification and technological advantages.
More companies are incorporating offsets into their climate strategies and are refining their offset procurement strategies.
Companies can develop a carbon offsetting strategy to proactively address their environmental impact, meet sustainability goals, enhance their reputation, comply with regulations, drive innovation, and potentially gain financial benefits.