
A renewable energy source
Biomethane is a 100% Renewable Natural Gas (RNG) produced from organic materials originating from the agri-food industry (food waste), agricultural and municipal waste, as well as sewage sludge and treatment plants.
The carbon intensity of biomethane is relatively low. This is because the greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) released when it is burned as energy is roughly equivalent to the amount of GHG avoided by turning it into energy. The minimal net carbon emissions make biomethane a more environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
Biomethane production
Producing biomethane typically involves a process called anaerobic digestion. The gas derived in this process uses only organic matter.
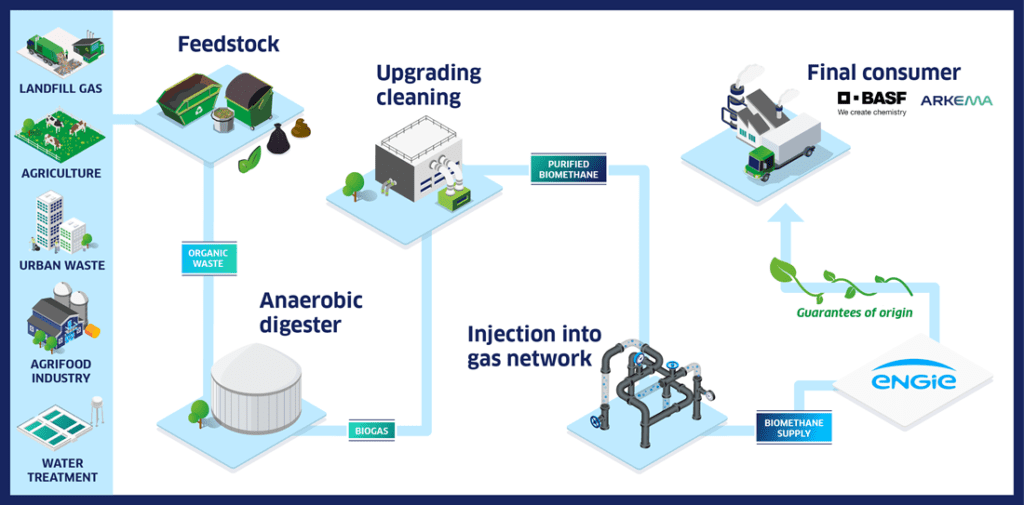
Biomethane production typically involves several steps. The key stages consist of the following steps:
- Aerobic Digestion: Organic wastes and residues are sorted, stirred, and fed into an anaerobic digester, also called a methanizer or biogas plant. The organic waste is mixed and heated in the digester. During the fermentation process, bacteria convert organic matter into biogas. Biogas is mainly made up of methane and carbon dioxide, with small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen, and water vapor. The exact composition of biogas can vary depending on the feedstock used and the conditions of the digestion process. Biogas is considered a green gas, since it is derived from organic materials. It can be used differently, including heating through combustion in a boiler or as a source of both electricity or heat through cogeneration.
- Upgrading Cleaning: Once the biogas is purified it reaches a methane concentration greater than 97%. This step is key to separating biomethane from impurities and other components of biogas like carbon dioxide, sulfur compounds, and water. After purification, the gas is analyzed by the network operator and gets a Guarantee of Origin (GO) and a Proof of Sustainibility (PoS) if the plant is certified.
- Injection: Due to its similar properties to natural gas, biomethane can be easily injected into existing natural gas pipelines and infrastructure, making it easier to integrate into the gas network. Once injected into the gas networks, biomethane blends seamlessly with natural gas, and they cannot be distinguished.
Contributing to the circular economy in your region
The energy crisis of 2022 highlighted the need to ensure supply security, price stability, and the availability of local, decarbonized energy sources.
The raw materials for biomethane production are sourced locally or regionally, often community-based or owned by local entities. This proximity reduces the necessity for long-distance transportation of feedstock, resulting in decreased energy consumption and emissions associated with transportation.
Additionally, local proximity stimulates the local economy by creating jobs in waste management and infrastructure development, providing an additional source of income for farmers.
Biomethane Purchase Agreements as a lever in renewable energy procurement
The European Parliament and the EU Council have established the Renewable Energy Directive (RED, REDII and now REDIII) establishing the ‘sustainability of bioenergy’ as a fundamental principle. This principle encompasses the production of biofuels, bioliquids, biogas, as well as electricity, heat, or cooling generated from biomass.
Biomethane Purchase Agreements (BPAs) between renewable gas producers and industrial gas consumers, most of the time via a midstreamer, have gained recognition as a valuable tool in gas procurement strategies.
The primary advantage for industrial gas consumers entering a BPA is the assurance of a stable, sustainable, and potentially cost-competitive gas supply
BPA agreements typically span 5-15 years, similar to Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs).
Leading the way in biomethane for a sustainable future
In our pursuit of decarbonization and a net-zero emissions future, ENGIE – International Supply & Energy Management has set an ambitious goal to become a leader in biomethane supply, aiming for 30 terawatt-hours (TW) by 2030. Biomethane is one of the solutions to our commitment to sustainability.
Our role extends beyond production; we assist our clients in their transition by facilitating access to The Guarantee of Origin (GO) system. This ensures transparency and traceability in renewable energy production, playing a crucial role in reducing CO2 emissions.
Like Arkema, which has signed a contract for the supply of 300 GWh/year of renewable biomethane in France, one of the largest private biomethane contracts in Europe to date, trust ENGIE to help you achieve your sustainable ambitions.
Antoine Sabatier, Head of Renewables Gas for ENGIE – International Supply & Energy Management, highlights “ENGIE’s commitment to this objective supports the transition to cleaner energy and solidifies our position as a leader in renewable energy and reinforces our dedication to a sustainable, low-carbon future“.